
Introduction
Dividend stocks are shares of companies that pay investors a portion of their profits. These payments, called dividends, are often sent out quarterly and can come in the form of cash or additional shares. For many investors, dividend stocks offer a simple way to earn passive income while also benefiting from potential stock price growth.
Companies that pay dividends are usually well-established and financially stable. They share their earnings with shareholders instead of reinvesting all profits into expansion. This makes dividend stocks attractive to those looking for a steady income, especially during retirement.
In this blog, we’ll break down what dividend stocks are, the different types of dividends, the key benefits and risks, and how to evaluate them before investing. If you’re looking to grow your money while earning regular payouts, this guide is for you.
1. What Are Dividend Stocks?
Dividend stocks are shares in companies that distribute part of their earnings to shareholders. For example, if you own stock in a company like Coca-Cola or Johnson & Johnson, you may receive quarterly cash payments just for holding the stock.
These dividends can be paid in two main forms: cash, which goes directly into your account, or additional shares of stock. Some companies even offer both options, depending on your investment preferences.
Most companies that pay dividends are stable and profitable. They operate in industries like consumer goods, utilities, or healthcare—sectors known for steady demand. Instead of using all profits to grow the business, these companies reward shareholders with regular payments. This approach helps investors build wealth over time while enjoying a passive income.
2. Key Characteristics of Dividend Stocks
📌 Regular Payments
Dividend stocks pay shareholders consistently—usually every quarter. That means four times a year, you receive a portion of the company’s profits. For example, companies like Coca-Cola and Procter & Gamble are known for their reliable dividend payouts. This makes dividend stocks a popular choice for people looking for a steady income.
📌 Dividend Yield
This tells you how much you’ll earn each year in dividends based on the stock’s price. It’s shown as a percentage. If a stock costs $100 and pays $4 per year in dividends, the yield is 4%. A higher yield may look attractive, but it’s important to check why the yield is high—it could be a warning sign if the stock price has dropped.
📌 Payout Ratio
The payout ratio shows how much of a company’s profits are being paid out as dividends. If a company earns $10 per share and pays $5 in dividends, the payout ratio is 50%. A healthy payout ratio—often between 30–60% %—suggests the company can afford the dividend and still has money to grow.
📌 Growth Potential (Dividend Aristocrats)
Some companies not only pay dividends—they increase them every year. These are called Dividend Aristocrats. To qualify, a company must raise its dividend every year for at least 25 years. Examples include Johnson & Johnson and McDonald’s. These stocks offer a growing income stream and are a sign of a strong, stable business.
3. Types of Dividends
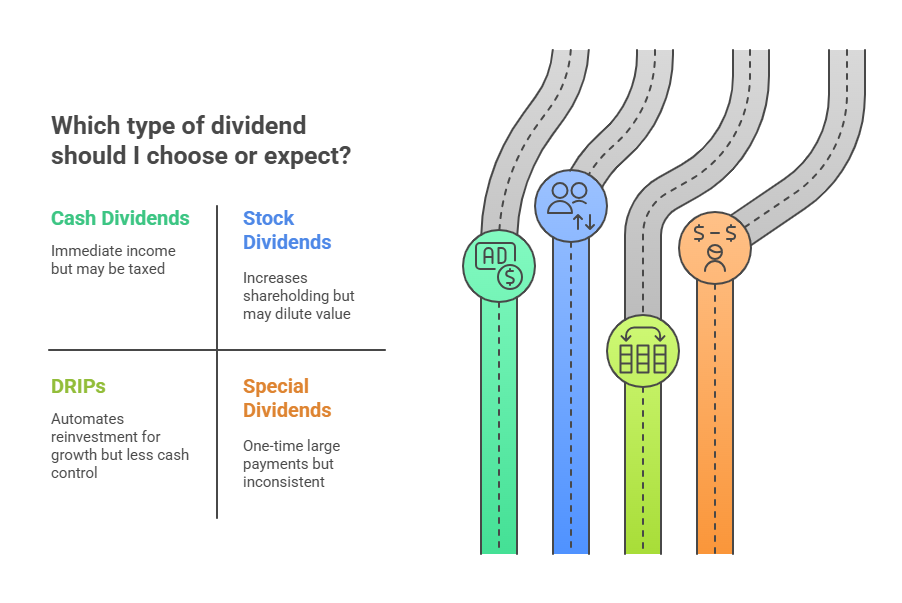
📌 Cash Dividends
The most common type. Companies deposit cash directly into your brokerage account. You can choose to spend it or reinvest it.
Pros: Immediate income.
Cons: You may be taxed depending on your situation.
📌 Stock Dividends
Instead of cash, you receive extra shares. For example, a 5% stock dividend means you get 5 extra shares for every 100 you own.
Pros: Helps grow your holdings.
Cons: Can dilute share value slightly.
📌 DRIPs (Dividend Reinvestment Programs)
These automatically reinvest your dividends into more shares of the same company, often at no commission and sometimes at a discount.
Pros: Easy way to grow investment over time.
Cons: Less control over cash flow.
📌 Special Dividends
One-time payments are made when a company has extra profits. These aren’t regular and can be large.
Pros: Surprise bonus for investors.
Cons: Not consistent or guaranteed.
📌 Preferred Dividends
Paid to holders of preferred stock, which has priority over regular (common) stock. These are fixed and predictable.
Pros: Reliable income stream.
Cons: Less potential for stock price growth compared to common shares.
Each dividend type has its purpose. Understanding how they work can help you decide which fits your investing goals best.
4. Benefits of Dividend Stocks
📌 Reliable Income Stream
Dividend stocks provide consistent payouts, making them a favorite for retirees and long-term investors. That quarterly income can help cover expenses or be reinvested to grow your portfolio.
📌 Compound Growth Through Reinvestment
Using a DRIP (Dividend Reinvestment Plan), you can reinvest your dividends to buy more shares. Over time, this creates a compounding effect. The more shares you own, the more dividends you earn, and the cycle continues.
📌 Potential for Long-Term Capital Appreciation
Many dividend-paying companies are stable and well-managed. This means their stock prices can grow steadily over time, in addition to paying dividends. It’s a win-win: growth + income.
📌 Indicators of Financial Strength and Confidence
Consistent dividends suggest the company is financially healthy. If a company raises its dividend regularly, it’s a sign that the leadership believes in the future performance of the business.

5. Risks and Considerations
📌 Dividends Can Be Cut or Suspended
Dividends are never guaranteed. If a company faces financial trouble, it may reduce or stop dividend payments. This can hurt both your income and the stock price.
📌 Dividend Traps
A very high dividend yield can be tempting—but it might signal a problem. If a stock’s price is falling quickly, the yield might look high even though the business is in trouble. Always research the reason behind a high yield.
📌 Slower Growth Potential
Some dividend-paying companies are in mature industries. This means they may not grow as fast as younger companies. While they offer stability, they might lag in explosive growth opportunities.
Dividend stocks are powerful—but like any investment, they come with trade-offs. Smart investors weigh the pros and cons before jumping in.
6. How to Evaluate Dividend Stocks
📌 Look at Dividend Yield in Context
Don’t chase the highest yield. A 3–-5 % dividend yield is often considered healthy. Compare yields within the same industry to understand if a stock’s return is competitive or a potential red flag.
📌 Check the Payout Ratio for Sustainability
This ratio shows how much of a company’s profit goes to dividends. A payout ratio under 60% is generally considered sustainable. If the number is too high, the dividend might be at risk during downturns.
📌 Review Dividend Growth History
Companies with a track record of increasing dividends—especially Dividend Aristocrats—are more reliable. Consistent growth shows strong management and financial discipline.
📌 Assess Financial Health and Industry Stability
Check a company’s debt levels, cash flow, and profitability. Strong financials support consistent dividends. Also, consider the stability of the industry. Utilities and consumer staples often offer more dependable payouts.
7. Ways to Invest in Dividend Stocks
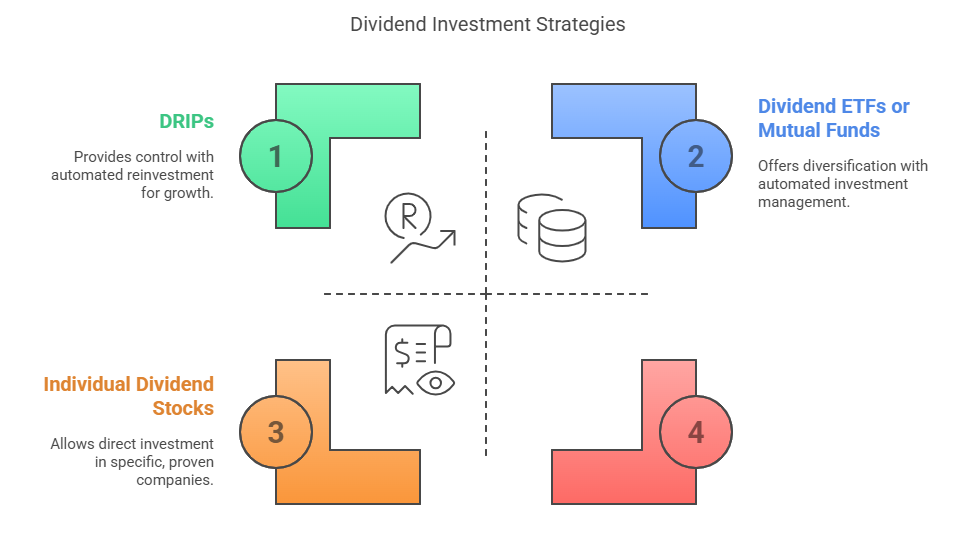
📌 Buying Individual Dividend-Paying Stocks
Invest in companies like Coca-Cola, Johnson & Johnson, or Procter & Gamble. You get control and the chance to focus on solid, proven businesses.
📌 Using Dividend ETFs or Mutual Funds
These funds group multiple dividend-paying stocks for instant diversification. Great for beginners or hands-off investors.
📌 Reinvesting via DRIPs
A DRIP lets you automatically use your dividends to buy more shares—no need to invest manually. Over time, this boosts your returns through compound growth.
Conclusion
Dividend stocks offer more than just cash—they’re a strategy for long-term financial growth. They provide a steady income, strong performance, and compounding potential. Whether you’re building wealth or planning for retirement, dividend stocks deserve a place in your portfolio.
Start simple. Do your homework. Whether through individual picks or dividend ETFs, taking the first step can lead to a steady stream of passive income and long-term success. 💸📈
